In 2020, the focus of World Hepatitis Day was preventing the transmission of hepatitis B virus from mothers to newborns. WHO requested ministers of health in countries of the Region to commit to eliminating mother-to-child transmission to ensure a hepatitis-free future for future generations and affirmed its support to countries to achieve hepatitis elimination targets.
Regional programmes for hepatitis, immunization, maternal and child health came together to identify strategies for governments to eliminate viral hepatitis as a major public health problem.


A key objective of this year’s campaign is to urge countries to take action by adopting coordinated strategies to achieve elimination of mother-to-child transmission of hepatitis B virus.
The 5 key hepatitis interventions proposed in the “Global health sector strategy on viral hepatitis 2016–2021: towards ending viral hepatitis" are:
vaccinating infants against hepatitis B;
preventing mother-to-child transmission;
ensuring injection and blood safety;
providing harm reduction services;
providing access to hepatitis B and C testing in view of treatment.
People living with hepatitis B infection in 2019 by WHO region
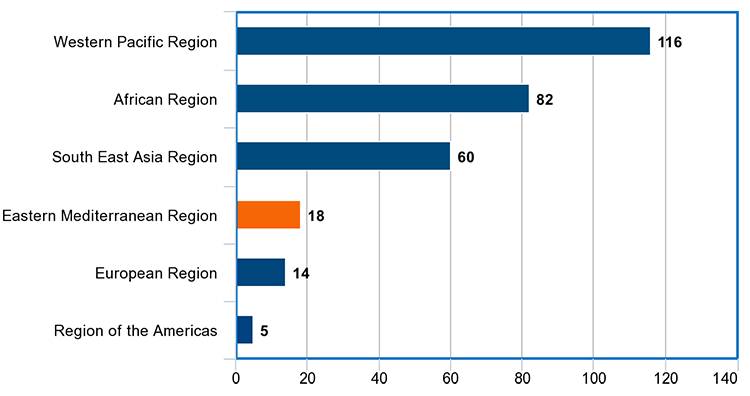
At the end of 2019, it was estimated that 18 million people in the Region were chronically infected with hepatitis B.
Prevalence of hepatitis B infection in the general population in 2019: 2.5%
[2.0–3.3%]
Prevalence of hepatitis B infection among children under 5 in 2019: 0.8% [0.5–1.1%]
Number of people estimated as dying from hepatitis B in 2019: 33 000
[26 000–60 000]
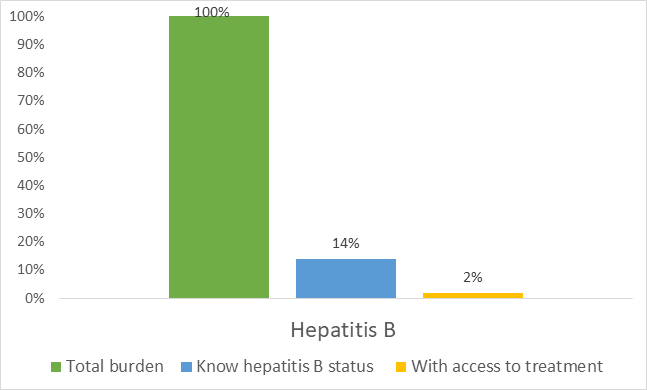
Percentage of total hepatitis B burden, people with knowledge of their status and access to treatment in WHO’s Eastern Mediterranean Region, 2019
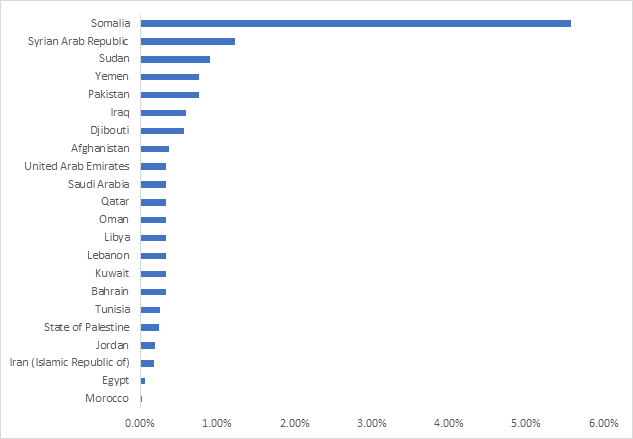
Prevalence of hepatitis B infection in children under 5 in countries of the Region, 2019

Regional Director's message
Our Region has led the way in hepatitis C testing and treatment over the last five years, thanks to strong political commitment from our Member States, especially Egypt. Twenty Member States have now achieved hepatitis B control targets, reaching less than 1% hepatitis B prevalence among children under five years of age. These successes prove that we can make a difference....

Social media cards












