Tobacco and sustainable development
How does tobacco use affect sustainable development?
Tobacco use has devastating health, social, environmental and economic consequences. It is a major barrier to sustainable development. Tobacco use impacts health, poverty, global hunger, education, economic growth, gender equality, the environment, finance and governance.
Each year, more than 7 million people die from tobacco use. This figure includes the 900 000 that die from exposure to secondhand smoke. Over 80% of these deaths occur in low- or middle-income countries. These countries bear almost 40% of the global economic cost of smoking from health expenditures and lost productivity, estimated at over US$ 1.4 trillion.
Campaign materials
Acting Regional Director's message
This year, World No Tobacco Day focuses on “Tobacco and Heart Disease”.
The campaign aims to increase awareness of the link between tobacco use in all its forms and cardiovascular disease, which is the world’s leading cause of death. At the same time, it highlights action that key audiences – including cardiovascular communities and specialists, governments and the public – can take to reduce the risks to heart health related to tobacco use.
Globally, cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death and disease in most countries in WHO’s Eastern Mediterranean Region. In 2015, nearly 1.4 million deaths in the Region were caused by cardiovascular disease. It has been estimated that in the next decade, deaths from cardiovascular disease, which in the Eastern Mediterranean Region is mostly attributable to ischemic heart disease, will increase more significantly than in any other region of the world except Africa.
Tobacco use in the Eastern Mediterranean Region is alarming. Around 38% of men and 4% of women are smokers, and smoking is expected to rise by 2025, contrary to the trend for all other WHO regions. This will lead to an escalating epidemic of cardiovascular disease regionally, as tobacco use is a key risk factor for the development of coronary heart disease, stroke and peripheral vascular disease.
The harms that all types of tobacco use can cause to heart health are well understood in medical and scientific circles, and solutions to reduce related death and disease are available, including full implementation of the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control. However, large sections of the public do not realize that tobacco is one of the leading causes of cardiovascular disease.
Countries in the Region need to take all possible action and make every effort to control tobacco use and raise public awareness of the link between tobacco use and heart disease. This will help to reduce cardiovascular disease in the Region.
WHO and its partners have developed technical packages to support countries in their efforts to limit tobacco use and so contain this cardiovascular disease epidemic at national and regional levels. Research has shown that 1.13 million deaths due to cardiovascular disease could be avoided in 20 low- and middle-income countries, including three countries in the Eastern Mediterranean Region: Egypt, the Islamic Republic of Iran and Pakistan.
WHO’s Global Hearts Initiative can save many millions of lives by ramping up proven measures to prevent CVD in communities and countries, including taxing tobacco, reducing salt in foods, detecting and treating people at high risk and strengthening primary health care services.
Nineteen countries in the Region are parties to the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control, the first evidence-based international treaty, and are obliged to implement its different policies comprehensively. This will reduce tobacco use and consequently cardiovascular disease levels in the Region.
On this World No Tobacco Day, I call upon everyone – governments, advocates, academics, cardiovascular specialists and civil society groups – to join efforts to end the tobacco epidemic and its devastating consequences.
Fact sheets
|
|
|
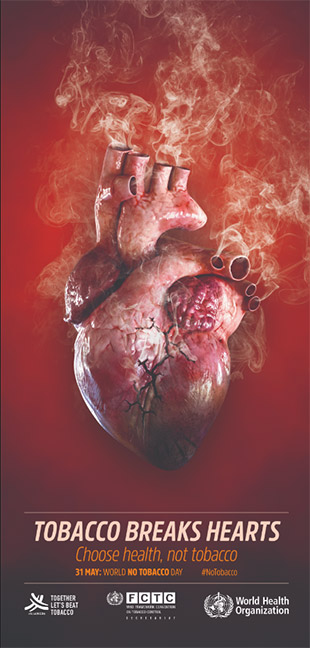
Poster: Tobacco breaks hearts
Video
How Smoking Affects your heart
Infographics, social media materials
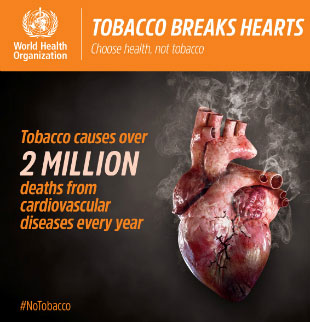
Cardiovascular diseases
Tobacco causes over 2 million deaths from cardiovascular diseases every year
[pdf, 12.2Mb]
[jpeg, 397kb]
Heart attacks and stroke
Eliminating tobacco use can prevent millions of people dying from heart attacks and strokes
Twitter/instagram [jpg, 402kb]

Heart disease
Hundreds of millions of tobacco users are unaware tobacco causes heart disease
Twitter/Instagram [jpg, 413kb]
Global health
Reducing tobacco use promotes global health and boosts development
Twitter/Instagram [jpg, 381kb]
Tobacco breaks hearts
Choose health, not tobacco
Twitter/Instagram [jpg, 669kb]
Rollup banner
Recommended actions for stakeholders

The scale of tobacco’s devastation of human health is shocking. The tobacco industry continues to aggressively promote the use of tobacco products and to conceal the dangers of tobacco use. But, we are fighting back to help prevent this ongoing devastation. We can prevent the daily deaths (more than 19 000) caused by tobacco use or second-hand smoke. By uniting, we can save lives and defeat tobacco, which is inherently harmful in all its forms.
WHO and its partners has developed technical packages to support countries in their efforts to limit tobacco use and so contain this cardiovascular disease epidemic at national and regional levels.
Countries need to:
fully implement these technical packages which together constitute the Global Hearts Initiative to scale up prevention and control of cardiovascular disease and includes:
MPOWER, a set of six practical, affordable and achievable measures to help countries implement specific provisions of the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control and so reduce demand for tobacco;
SHAKE, a new set of evidence-backed policy options and examples to support governments in lowering consumption of salt among their populations; and
HEARTS, a technical package that gives countries the tools to incorporate best practices in cardiovascular disease management at the primary health care level to reduce risk factors such as high blood pressure and high blood cholesterol.
Countries and civil society need to:
take all possible action and make every effort to control tobacco use and raise public awareness of the link between tobacco use and heart disease.
combat tobacco industry interference in political processes, in turn leading to stronger national tobacco control action.
Public and partners need to:
participate in national, regional and global efforts to develop and implement strategies and plans and achieve goals that prioritize action on tobacco control.
Individuals need to:
contribute to making a tobacco-free world, either by committing to never taking up tobacco products, or by quitting the habit.
WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control
MPOWER: technical package to defeat the global tobacco epidemic
SHAKE: technical package for salt reduction
HEARTS: technical package for cardiovascular disease management in primary health care








 [
[