On World Obesity Day, 4 March, the World Health Organization is calling on everyone to take action to combat the obesity epidemic by working together to address its many root causes to create happier, longer and healthier lives. By raising awareness and improving access to appropriate information, we can combat this disease now and post-COVID-19, especially in low- and middle-income countries, in which obesity is rising fastest. Obesity can be prevented and treated through the adoption of healthy lifestyles. Raising people’s awareness of the links between lifestyle and obesity, and COVID-19 complications and obesity, can not only reduce the burden but empower people to make healthy lifestyle choices, such as keeping physically active and choosing healthy food and drinks.
The obesity epidemic
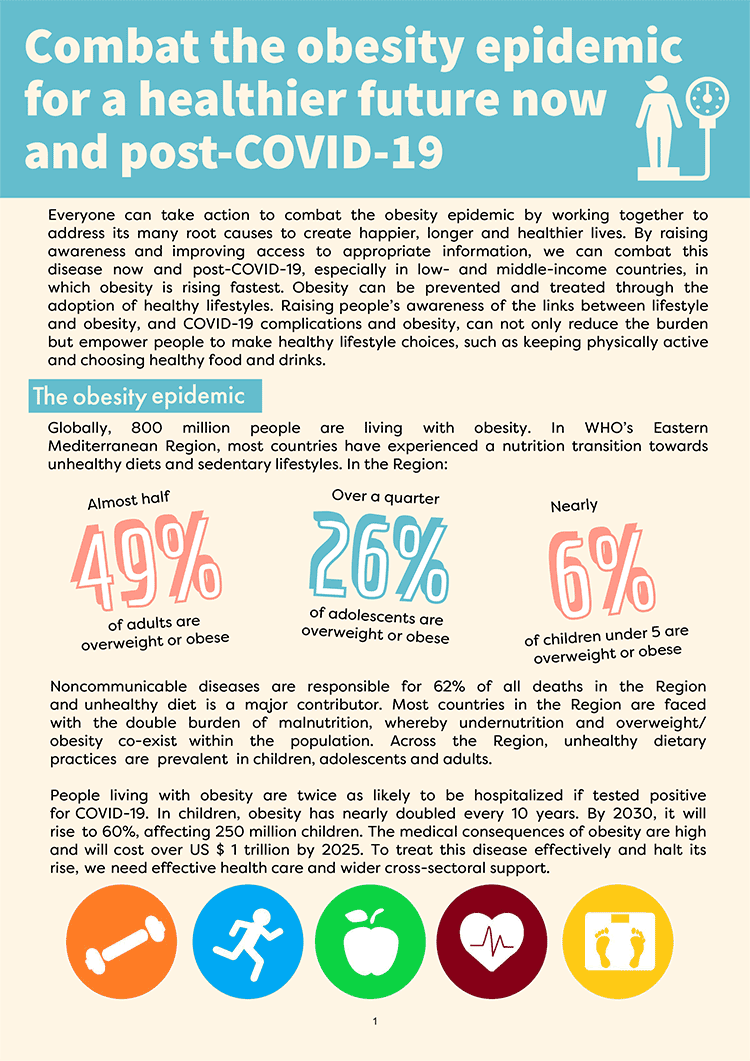
Globally, 800 million people are living with obesity. In WHO’s Eastern Mediterranean Region, most countries have experienced a nutrition transition towards unhealthy diets and sedentary lifestyles. Almost half the Region’s adults (49%), over a quarter (26%) of adolescents and nearly 6% of children under 5 are affected by overweight or obesity. Noncommunicable diseases are responsible for 62% of all deaths in the Region and unhealthy diet is a major contributor. Most countries in the Region are faced with the double burden of malnutrition, whereby undernutrition and overweight/obesity co-exist within the population. Across the Region, unhealthy dietary practices are prevalent in children, adolescents and adults.
People living with obesity are twice as likely to be hospitalized if tested positive for COVID-19. In children, obesity has nearly doubled every 10 years. By 2030, it will rise to 60%, affecting 250 million children. The medical consequences of obesity are high and will cost over US $ 1 trillion by 2025. To treat this disease effectively and halt its rise, we need effective health care and wider cross-sectoral support.
Risks of obesity
People living with obesity are at greater risk from noncommunicable diseases, such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease and certain cancers, as well as mental health illnesses (because of weight stigma), and COVID-19 complications and death.
Preventing and treating obesity is not just about losing weight, it is about adopting healthier behaviours to manage this disease and improve overall health. Equally as important is supporting appropriate nutrition for children to prevent and treat childhood obesity otherwise, it carries through into adulthood. Obesity in children affects their physical health, social and emotional well-being, and self-esteem. It is also linked to poor academic performance and a lower quality of life.
Root causes of obesity
Obesity is not anyone’s fault. Weight gain is often driven by a variety of factors that are outside people’s control such as biology, mental health, genetic risk, life events, environment, access to health care, marketing and access to ultra-processed food. Obesity is not caused by a lack of willpower.
Obesity and COVID-19
Obesity is now a major factor in COVID-19 complications and deaths. At the 2020 Global Obesity Forum, the global obesity community came together to acknowledge the complexity of this disease and developed the ROOTS approach, which sets out an integrated, equitable, comprehensive and person-centred approach to addressing obesity. Building on the ROOTS approach, the global obesity community issued a declaration that sets out recommendations for immediate action across the obesity spectrum from prevention to treatment, within the context of COVID-19.
Recognizing that obesity is a disease in its own right, as well as a risk factor for other conditions, including significantly worsening the outcomes of COVID-19 infection.
Obesity monitoring and surveillance must be enhanced to strengthen effective strategies for preventing and treating obesity.
Obesity prevention strategies must be developed, tested and implemented across the life course, from pre-conception, through childhood, and into older age.
Treatment of obesity – including behavioural, pharmacological, digital, nutritional, physical activity based and surgical interventions – should be accessible to all people with obesity.
Systems-based approaches should be applied to the treatment and prevention of obesity.
Obesity prevention and control
It is possible to prevent and control obesity but we need action on all fronts. We need to raise awareness and improve access to the appropriate information to ensure happier, longer and healthier lives for everyone now and in our post-COVID-19 future. There is a need for health systems to address obesity prevention and treatment through strengthening health systems and moving towards universal health coverage. There is also much work to be done on prevention in terms of both public education and policy action.
The regional framework for action on obesity prevention 20192023, a road map for countries of the Region to implement the action areas of the United Nations Decade of Action on Nutrition, is central to accelerating action on obesity prevention and control. It sets out 6
key action areas for improving nutrition and food security:
sustainable, resilient food systems for healthy diets;
aligned health systems providing universal coverage of essential nutrition actions;
social protection and nutrition education;
trade and investment for improved nutrition;
safe and supportive environments for nutrition at all ages; and
strengthened governance and accountability for nutrition.
Call to action
This World Obesity Day:
• Governments can provide and improve access to quality obesity care, as well as develop and effect policies that promote and normalize healthy eating and living, in addition to banning marketing of unhealthy foods and beverages high in fat, sugar and salt.
• Civil society groups, including nongovernmental organizations and the media, can work with individuals and communities to educate and diffuse key messages on the root causes of obesity, the importance of prevention and treatment, as well as the impact of adopting healthy behaviours like keeping physically active and choosing healthy food and drinks.
• Health care professionals, whether working directly in obesity care or supporting and working with those living with obesity, can learn more about obesity, expand their knowledge and have up-to-date, evidence-based obesity management resources to help them understand and address the root causes of this disease.
• Individuals and families can adopt healthier behaviours, share experiences, as well as ask for support and support others to improve their health and well-being and that of their children.
On World Obesity Day and beyond, everyone can take action and make change. Everyone can play a role in combating the obesity epidemic to create a healthier future now and post-COVID-19.
Related links
World Obesity Day 2021: Every body needs everybody
Support for health care professionals to learn more about obesity
Regional framework for action on obesity prevention 2019–2023
Global Obesity Forum Declaration 2021